Cryptocurrency is internet-based money secured by cryptography and run by open, public networks, not banks.
Key Features (No Jargon)
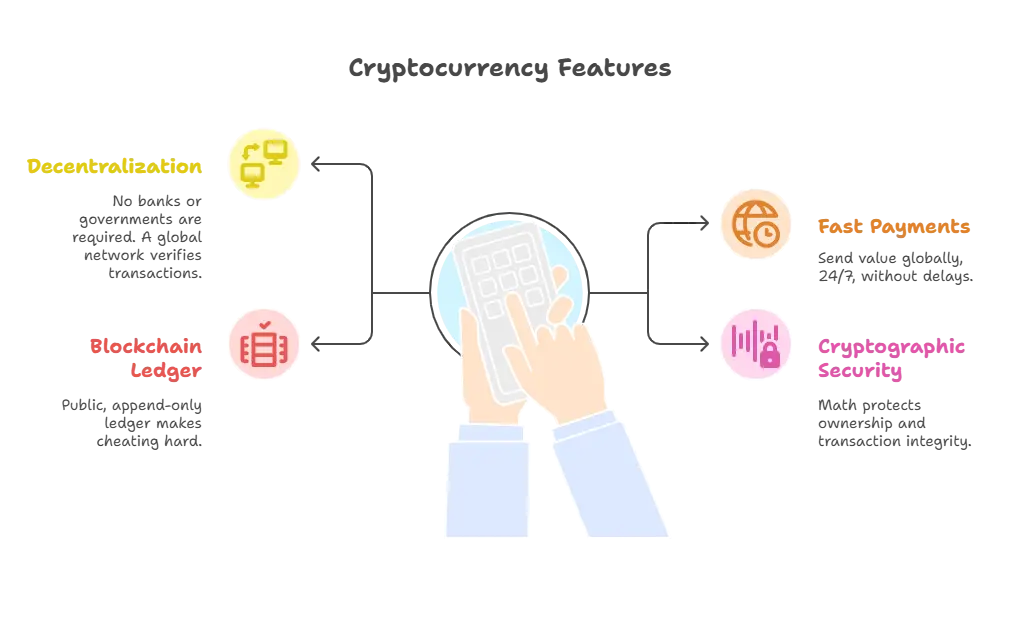
- No banks or governments required: Instead of a bank keeping score, a global network of computers verifies and records every transaction. Anyone can join, no single company or country controls it.
- Fast, global payments: Send value to anyone, anywhere, 24/7, no business hours, wire cutoffs, or typical bank delays.
- Blockchain “notebook”: Think of a public, append-only ledger: once a transaction is written, it’s locked in and visible to all, making cheating extremely hard.
- Secured by cryptography: Powerful math (hashing and digital signatures) protects ownership and transaction integrity, making forgeries and fakes impractical.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
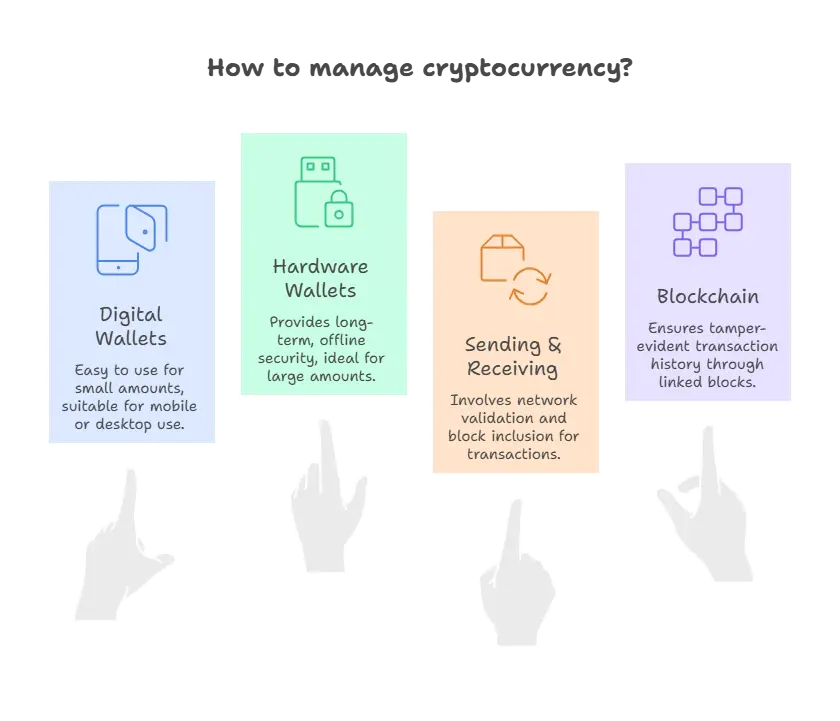
- Digital Wallets: A crypto wallet is like a money app for the internet. It stores your public address (where people can send you crypto) and your private keys (the secret that proves it’s yours). Basic types: mobile/desktop wallets (easy, great for small amounts) and hardware wallets (USB-like devices for long-term, offline security).
- Sending & Receiving: To pay someone, your wallet creates a signed message saying “send X to this address.” That message is broadcast to the network, where nodes check the signature and your balance. If valid, the transaction is picked up for inclusion in the next block.
- Blockchain: Transactions are grouped into blocks. Each block references the one before it, forming a tamper-evident chain. After network validation, the block is added permanently; reversing it would require impractical amounts of computing power.
- No Middlemen: Instead of a bank approving transfers, the network reaches consensus, a built-in rule system that all nodes follow. Honest majority wins; invalid transactions are rejected automatically.
Why Do People Care?
- Investment: Some see crypto as “digital growth assets.” Prices can rise sharply, but also fall just as fast. Volatility is part of the deal; never invest more than you can afford to lose.
- Alternative Payments: Crypto enables direct, peer-to-peer payments worldwide, no bank accounts, card processors, or business hours required, wherever it’s accepted.
- Decentralization: No single company or government controls the network. That can reduce single-point failures and offer a measure of censorship resistance for lawful transactions.
- Privacy & Security: You control your keys and don’t need to hand over personal details to transact on-chain. Trade-offs: key custody is your responsibility, and public blockchains are transparent by default.
What Makes Crypto Different From Regular Money?
Regular Money | Cryptocurrency |
Printed/issued by governments | Issued by open networks/computers |
Bank accounts + intermediaries | Peer-to-peer, no bank required |
Physical + digital records | Purely digital assets |
Closed ledgers, limited view | Public ledger, transparent by default |
Is Crypto Safe?
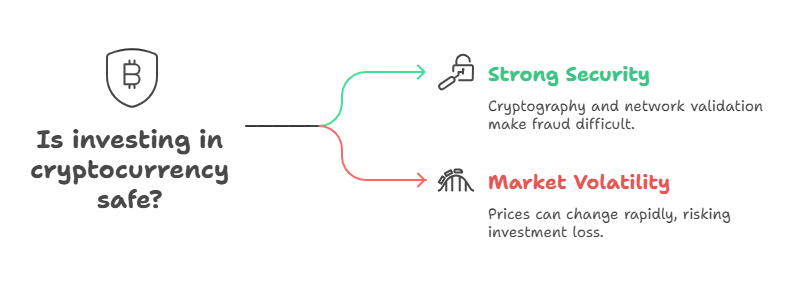
- Tech/security layer: Strong cryptography (hashes, digital signatures) and network validation make forged transactions and double-spends highly impractical.
- Market risk: Prices are volatile and can swing sharply in short periods, only invest what you can afford to lose.
Operational risk: You’re responsible for key management; scams/phishing and mistakes can permanently cost funds, “lose keys, lose funds.”